Revolutionizing RF MEMS Switch Technology
RF MEMS switches: tiny devices for high-performance, low-power RF signal control. ADGM1304 by Analog Devices is a popular choice. Used in wireless communication, radar, aerospace, defense, and medical devices. Major manufacturers: Analog Devices, GE, JFW OMRON, Samsung, Intel. Increasing demand drives R&D and patent filings, vital for market competitiveness.
RF MEMS (Radio Frequency Microelectromechanical Systems) switches have been a consistent replacement to electromechanical relays over past 20 years. Thus, revolutionizing electronic systems by providing an easy to use, switch that can operate on frequency ranging few megahertz to several gigahertz with minimal losses. RF MEMS switches are perfect for portable wireless and low-power, battery-operated systems because of their tiny size, good linearity, low insertion loss, high isolation, and exceptionally low power consumption. The RF and telecommunications industry in China has massively invested in the development of RF infrastructures and devices supporting 5G signals. China has gradually filled the technological gap that existed between its products and moved the epicenter of the 5G industry from the US to its shores. Overall, the increase in patent filings in the field of RF MEMS switches reflects the growing interest in this area of technology and the significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the years to come. As the market continues to evolve, it will be important for companies to stay on top of the latest technological developments and IP trends to stay competitive and take advantage of new growth opportunities.
RF-MEMS switches may either be capacitive or metal-to-metal type in terms of type of connection. Capacitive switches are better compared with the metal-to-metal types due to their ability to transmit signals of higher frequency and power. RF MEMS switches (as shown in Figure 1) use a micro-electromechanical structure to control the flow of RF signals. RF MEMS shunt capacitive switch with a unique spring design is shown in Figure1 (a). Typically, the structure includes a moving metal plate or beam hanging over a stationary metal plate. In the OFF state, the beam does not attach to the transmission line due to the presence of a thin dielectric layer and it gets released easily. The moveable plate slides towards the fixed plate when a voltage is supplied to the structure, forming a contact (ON - state) that allows the RF signal to flow through. The movable plate returns to its initial position after the voltage is turned off, breaking the contact, and stopping the RF communication as shown in Figure 1 (b).
Figure 1. RF MEMS Switch (a) Equivalent circuit diagram source
Figure 1. RF MEMS Switch (b) Structural diagram source
RF MEMS Switch Fabrication
RF MEMS switches are devices that use mechanical movement to switch RF signals on or off. Figure 2 shows several key steps involved in fabrication process of RF MEMS switches:
Figure. 2 RF MEMS switches Fabrication (a) Process source
Figure. 2 RF MEMS switches Fabrication (b) Packaged Switch source
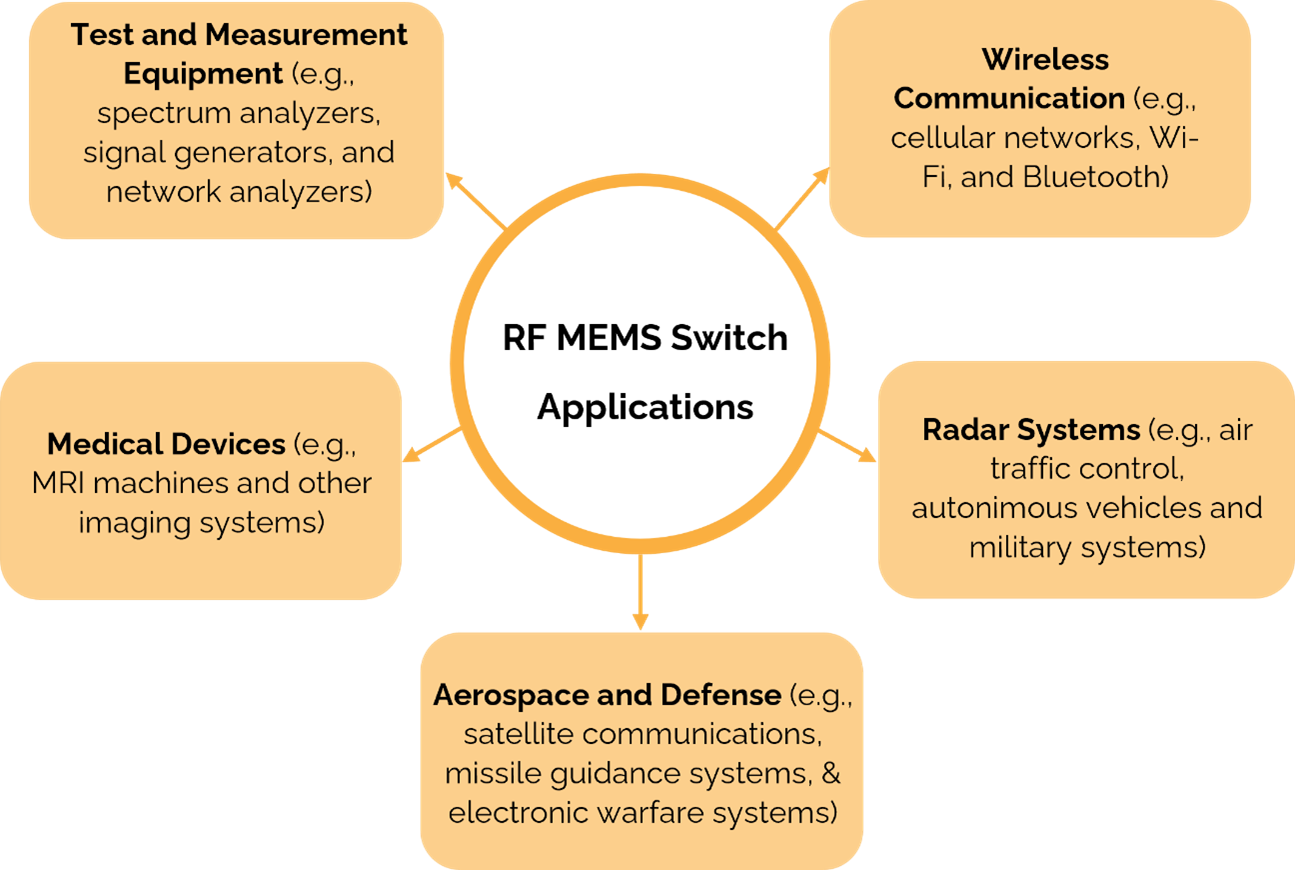
Applications of RF MEMS Switches
The high-frequency switching capabilities of RF MEMS switches make them well-suited for the applications mentioned above (Figure 3), and their compact size and low power consumption make them attractive for use in a wide range of devices. As a result, a significant amount of investment in this technology and a growing number of patents are being filed to protect these applications.
ADI MEMS Switch Technology
With MEMS, ADI has a long history. The ADI ADXL50 accelerometer, introduced in 1991, was the first MEMS accelerometer device to be successfully developed, manufactured, and commercialized worldwide. In 2002, ADI introduced the ADXRS150, the first integrated MEMS gyroscope. From these humble origins, ADI established a sizable MEMS product industry and an unsurpassed reputation for producing high-quality, dependable MEMS products. For use in automotive, industrial, and consumer applications, ADI has supplied more than one billion inertial sensors. This heritage provided the knowledge and conviction to advance MEMS switch technology to realization. The ADGM1304 is a widely used integrated RF MEMS switch designed by Analog Devices. It is designed for applications that require high-performance RF switching, including wireless communications, radar systems, test and measurement equipment, aerospace and defense, and medical devices. Figure 4 shows the cut-through view of the ADGM1304 switch. Figure 3 shows the functional diagram of ADGM1304. The ON/OFF position of the RF1 to RF4 switches shown in figure 3 corresponds to the selection of RF signals.
Evaluation Board Hardware
Figure 6 Evaluation kit for ADGM1304 source
The ADGM1304 evaluation kit shown in figure 6 shows a fully fitted, printed circuit board (PCB). that allows the user to connect RF signals to the MEMS switch. The user controls the switch operation using the on-board links or by applying the proper control signals to the appropriate connectors. The EVAL-ADGM1304SDZ provides an additional transmission line to facilitate the calibration of the network analyser to minimize the effects of the PCB tracks that connect the RF signals to the MEMS switch. Figure 7 shows various applications of ADGM1304 switch.
Figure 7. Application of ADGM1304 Switches
Few global manufacturers of RF MEMS Switch include:
Delf MEMS
Teledyne DALSA
Tronics
Analog Devices
GE Inspection Technologies
JFW Industries Inc., Skyworks
OMRON, RF Micro Devices
IP landscape and Industry Overview
The market for RF MEMS switches is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance switches in various applications. Samsung Electronics, Panasonic, Tokyo Electron, Robert Bosch, Apple, Qualcomm, Raytheon and Toshiba hold a significant number of patents/pending application related to RF MEMS switch technology as shown in Figure 8.
Top 10 Global Assignees in RF MEMS Switches
Figure 8. (source)
Figure 9 shows the technologies that involve the patent applications for RF MEMS switches. The major applications being Telecommunications. Key growth drivers include the increasing adoption of 5G wireless technology, the growing demand for wireless connectivity in IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and the increasing use of RF MEMS switches in medical and aerospace applications.
Technologies that involve RF MEMS Switch
Figure 9. (source)
Figure 10 shows the distribution of patents for RF MEMS switches in the past 10 years. The increasing demand for high-performance, low-power RF switching in a wide range of applications has led to constant research and development efforts in the field of RF MEMS switches. According to data from Orbit Intelligence, the number of patent applications related to RF MEMS switches has grown steadily over the past decade. In 2013, there were approximately 1058 patent applications related to RF MEMS switches filed globally. By 2019, this number had grown to 1764, reflecting a decent increase in the number of filings over the period.
Count of Patent/pending application*
Figure 10. For the past ten years in RF MEMS Switch (source) *Note: The count of patents for last two years might not be accurate due to unpublished applications.
Overall, the RF MEMS switch industry represents an exciting and rapidly evolving market, with significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the years to come. As the market continues to evolve, it will be necessary for companies to stay on top of the latest technological developments and IP trends to stay competitive and take advantage of new growth opportunities.
Conclusion
One of the main challenges with RF MEMS devices is handling high power in its compact size and developing reliable and cost-effective manufacturing processes that can meet the high-volume production requirements of the market. RF scientists are exploring developing RF MEMS devices with better material quality and capacity to withstand high power. Inventions in the area will again come up with a more significant number of patents and their related products. While there has been significant progress in this area in recent years, there is still room for innovation and improvement, particularly in wafer-level packaging, testing, and reliability.
References
Ansari, Hamid Reza, and Saeed Khosroabadi. "Design and simulation of a novel RF MEMS shunt capacitive switch with a unique spring for Ka-band application." Microsystem technologies 25.2 (2019): 531-540.
Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
Author
Dr. Shalini Mishra
Associate Consultant at Lumenci
Shalini works as an Associate Consultant at Lumenci. Her area of interest is Power electronics and Electrical Drives and condition monitoring of Transformer Insulation. She holds a PhD and a master’s degree from IIT(ISM) Dhanbad.