The transition from 4G to 5G Network
Wireless communication is a movement of information between two points without any physical medium. This type of communication occurs through space where antennas transmit and receive signals. With the advent of wireless communication technology, the cost of physical infrastructure has reduced, and people can communicate irrespective of their location. Also, the evolution in wireless communication has brought improved speed and widespread connectivity, even to remote areas. Wireless communication has thus far evolved in the following generations - 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G.
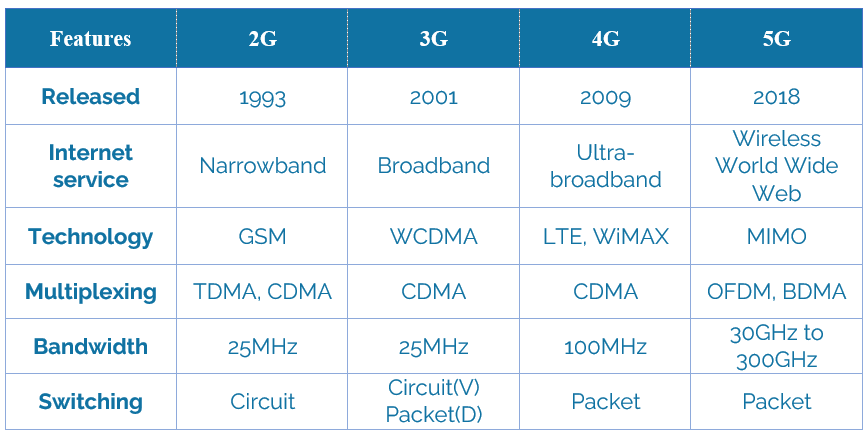
Evolution of cellular communication technology over the years (Source : Lumenci)
4G Wireless Network
4G is a 4th generation wireless network. It is faster than 3G but not as fast as 5G. With the help of the 4G network, users can watch HD videos on their mobile phones, which revolutionized smartphones and gave them functionality equivalent to computers. Now stable speed can be maintained with the help of 4G. 4G is usually described by the acronym “MAGIC.” MAGIC stands for Mobile multimedia Anytime/Anywhere Global mobility support, Integrated wireless, and Customized personal service. The technology behind 4G is LTE-Advanced.
What is LTE?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution. It was a significant step forward for the communication industry. LTE was developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). LTE uses the multiuser variant of OFDM modulation called OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) for the downlink signal. It allows the LTE downlink to transmit data from the base station to multiple users at data rates higher than the previous generation. For uplink signal, single-carrier FDMA is used, which lowers the transmit power needed of the user terminal.
4G Wireless network features (Source : Lumenci)
5G Wireless Network
Why 5G?
5G is the 5th generation wireless network. Machines and devices can be virtually connected using 5G. It is the most robust and fastest one among the world's technologies. It is used in areas like IoT and mission-critical communications. The standards for the usage of 5G are defined and driven by 3GPP. 5G will play a huge role in making technologies like Mixed Reality and Augmented Reality mainstream as it promises real-time computing. We can say, with 5G, the much-anticipated metaverse can become a real thing.
Characteristics
It has a very high speed (up to 10 Gbps).
It uses shorter frequencies and higher bandwidth.
It has low latency and high quality.
Drawbacks
It is available in only some locations and thus has limited global coverage.
Less broadcast distance as compared to 4G.
There is a huge battery drain in mobile phones that uses 5G.
A database can be stolen easily with an increase in bandwidth.
Areas of application
Internet of things (IoT): 5G can connect IoT devices at a higher speed and make autonomous vehicles a reality.
As 5G has low latency, VR and AR applications are more interactive.
Smart City Infrastructure and Traffic Management.
5G will enhance the usage of drones.
How is 5G Different from 4G
5G has lower latency which is under 5 milliseconds. On the other hand, the latency of 4G ranges from 60 to 98 milliseconds. High latency means a delay in data transmission, while low latency means good network speed.
The download and upload speed of 5G is more than 4G.
5G has better bandwidth than 4G. 5G uses a 100 to 800 MHz channel. On the other hand, 4G uses a 20 MHz channel.
5G provides more security than 4G.
Effect of 5G on Global Economy and Other Aspects of People’s Lives
5G pays a significant contribution to changing the global economy. It is known from a recent study that applications of 5G in financial service will add USD 85 billion to the global GDP by 2030. The reason behind this is the digitization of banks and mobile banking. By using 5G technology in drones, insurance industries can monitor insured properties and stop fraudulent practices. Also, the number of IoT-connected devices will likely jump to 70 billion by 2025, most of which are used in industrial applications. With more interconnected devices in innovative industries, 5G has marked an era of automation.
Development of metaverse can be enhanced with growing access to 5G as it provides the necessary power and speed to support a fully digitalized world. 5G supporting devices are being manufactured by companies so that we can have devices to support metaverse activities. Presently, we need fast Wi-Fi to live in the metaverse. 4G does not provide sufficient bandwidth, so it cannot support metaverse aggressively. We need the speed of 100s of Mbps (i.e., more than 100 Mbps) to connect to the metaverse. We currently have AR and VR devices connected to cable, but we should aim for headsets as simple as ordinary eyeglasses and wireless for more convivence. 5G is the solution to this problem. With the help of 5G, the need for heat-generating components can be removed from the headset, and they can be made more compact and advanced, and less bulky.
5G is expected to have a strong connection with the real-world economy. As we adopt 5G, a new virtual world comes knocking on our door. It will allow companies and individuals to participate in economic activity the same way today. Physical presence will start getting obsolete. The creation of the Metaverse will act as a catalyst for developing blockchain systems oriented towards decentralized governance, decentralized finance, and smart contracts in general. It is forecasted that over 50% of today’s children will have jobs that don’t exist currently. Most of them could be related to the metaverse. 5G technology will play a critical role in making all of this happen.
*Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and is considered to be reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
*Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and is considered to be reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
Author
Editorial Team at Lumenci
Through Lumenci blogs and reports, we share important highlights from the latest technological advancements and provide an in-depth understanding of their Intellectual Property (IP). Our goal is to showcase the significance of IP in the ever-evolving world of technology.