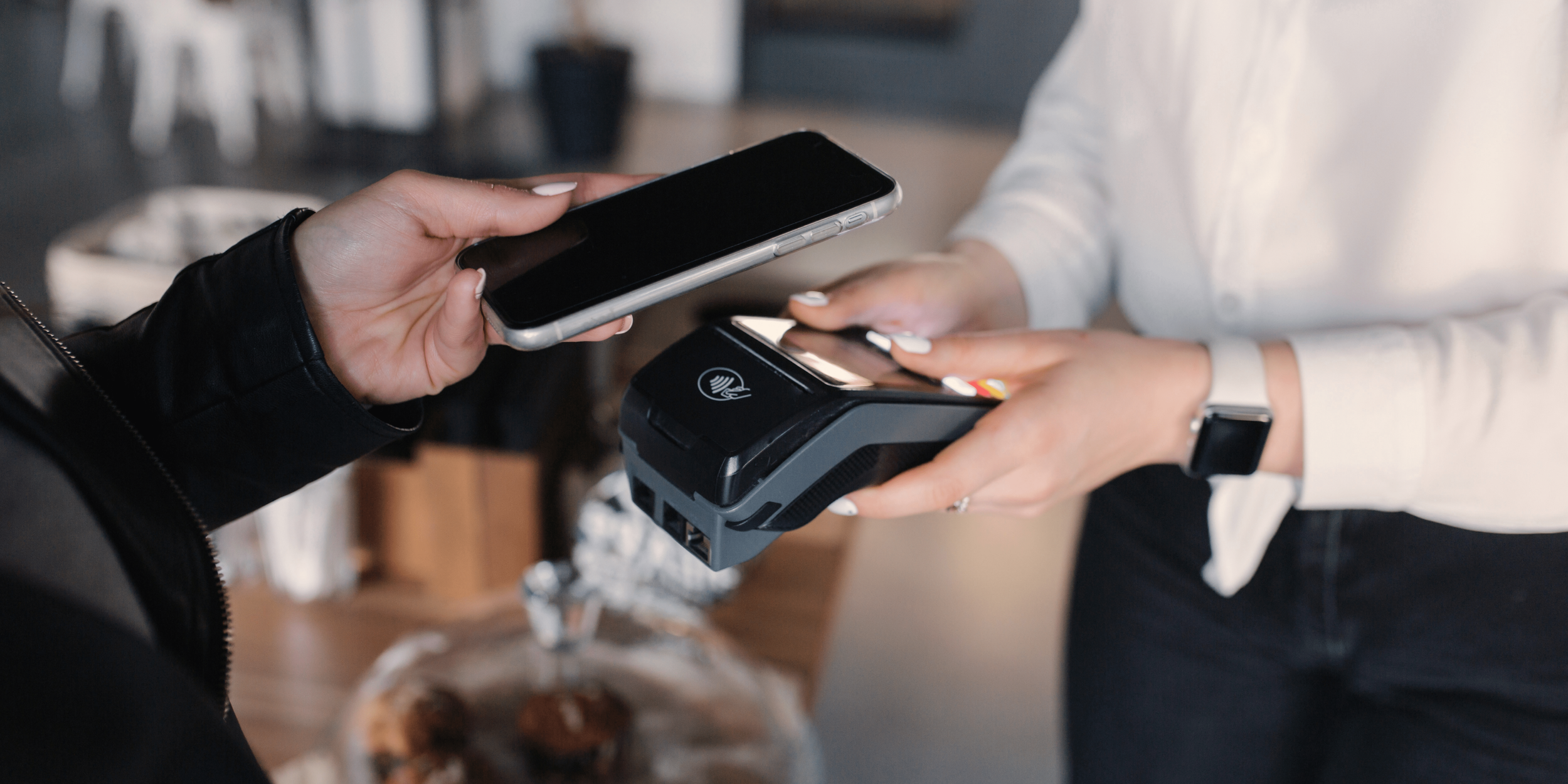
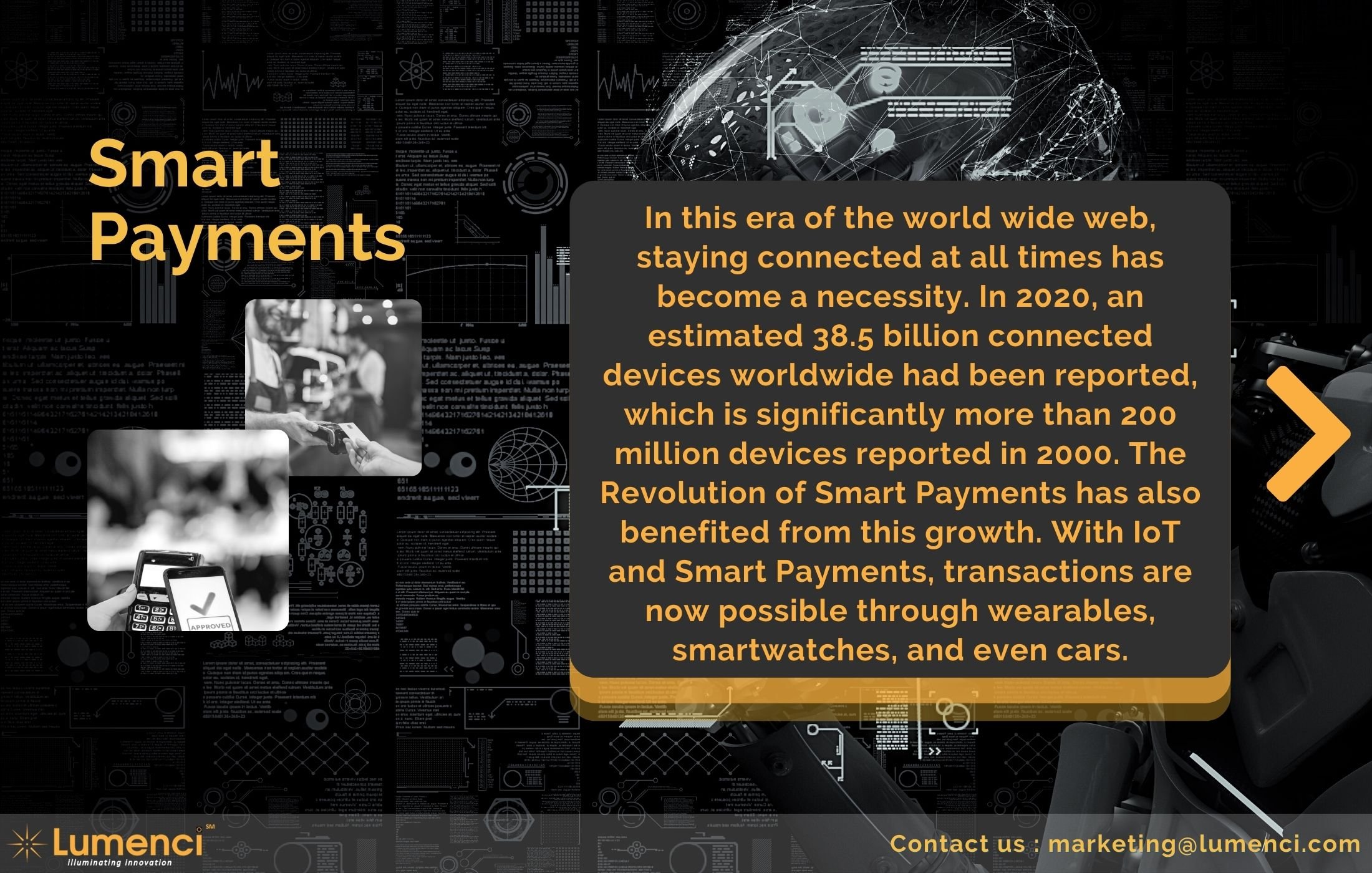
Digital Payments
Digital payment is the transfer of value from one payment account to another via digital devices such as a mobile phone, computer, credit, debit, or prepaid card between the payer and the payee.
History of Digital Payments
Western Union introduced the first Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT) in 1871, marking the beginning of the modern era of electronic payments. Since then, making purchases without physically making the purchase has gained widespread popularity. Electronic payment systems have progressed because of technological advancements. Making a transaction now requires a little more effort than tapping a button on a smartphone. It has been a struggle to achieve progress in simplifying payment processes.
Changing payment practices occurred gradually but steadily from the 1870s until the late 1960s. The Federal Reserve of the United States first used the telegraph to send money in the 1910s. Diner's Club International was the pioneering independent credit card company, paving the way for American Express to emerge a decade later. The first plastic credit card was issued by American Express in 1959.
It was only at the dawn of the 1970s that the widespread use of computers in the retail sector became commonplace. The Automated Clearing House (ACH) was created in 1972 to simultaneously handle enormous numbers of transactions. Not even two years later, NACHA standardized the process of ACH transfers.
Benefits of Digital Payments
Digital Payments increase the ease and convenience of the user as they don’t need to carry cash around and can pay with the ease of a button.
Digital Payments eliminate the need for cash management, lowering the risk of theft and reducing the cost of security and storage.
Digital Payments ease the accounting process, helping simplify operations and tax compliance.
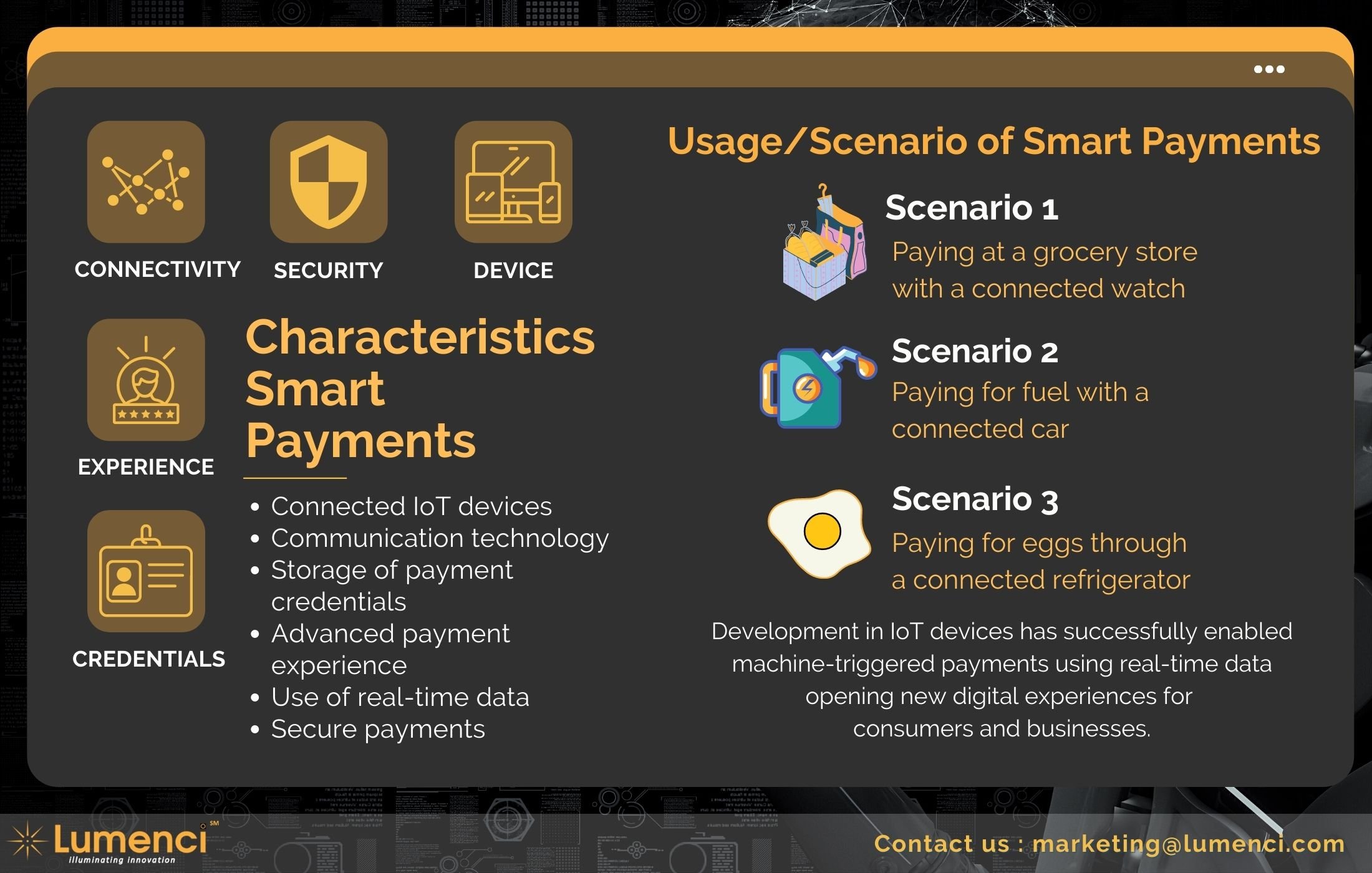
Different Methods of Digital Payments
Banking Cards
Banking cards give people more security, convenience, and control over their money than any other way to pay. There are many kinds of cards, like credit, debit, and prepaid, which gives you many options. Some types of card payment systems are RuPay, Visa, and MasterCard. People can buy things with payment cards in stores, online, through mail-order catalogs, and over the phone.
Mobile Wallet
A mobile wallet is a way to store digital cash on your phone. You can link your mobile device's credit card or debit card information to a mobile wallet app, or you can transfer money online to your mobile wallet. You can pay for things without using a plastic card. Instead, you can use your phone, tablet, or smartwatch. To put money in a digital wallet, it must be linked to a person's account. Most banks and some private companies have e-wallets, such as PayPal, Zella, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Paytm, Citrus Pay, Vodafone M-Pesa, ICICI Pockets, SpeedPay, etc.
Electronic Bank Transfers
Electronic fund transfer is the process of moving money from one bank account to another without the help of a bank employee. This can happen within the same financial institution or between different institutions. E.g.e.g., NEFT, RTGS, IMPS, e-transfer, electronic checks, etc.
Parties Involved in Digital Payments
Consumer’s bank (payer)
Merchant’s bank (payee)
Payment Network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard, Rupay, etc.)
Payment Gateway (e.g., Afterpay, Amazon Pay, Razorpay, Paytm, etc.)
Types of Digital Payments
1. Offline Payments
The payment is made in several steps when the card is swiped through the POS machine. Since the payee's debit card is being used to make the payment, the PoS provider checks to see if he has enough money in his bank account. This only happens after the payee enters the transaction PIN, which is limited. If there is enough money in the payee's account, the digital payment is processed, and the money is taken out of his account and put into the payer’s business account. If a credit card is used to make a digital payment, the card provider of the payer checks the available credit limit before the transaction goes any further.
2. Online Payments
When a payee buys something from an eCommerce portal, the eCommerce player sends a payment request to the payment gateway it has partnered with. Then, the payment gateway asks the payee for permission with an OTP or PIN, accepts the amount from her bank, and settles the amount with the bank where the e-commerce portal has an account. First, the gateway must check how much money is in the payee's bank account. If more money is in the history of the payee giving the wrong payment information, the request will be allowed.
Disadvantages of Online Payments
Technical Problems
Like any other technology-dependent software, online payment systems are vulnerable to downtime and technical difficulties. Customers who shop online may become irritated if a service is temporarily unavailable due to a tech maintenance operation, even if they are informed in advance, and the work is performed at night. Businesses often see high bounce rates when this occurs unexpectedly.
Password Threats
A website's online portal may be able to access your personal information or bank account details if you are a registered user and make frequent online payments. Password protection is necessary despite the widespread use of OTPs (one-time passwords) for most financial dealings. If you do business with multiple institutions, your personal information could be at risk.
Cost of Fraud
Cybercriminals are adapting to the growing trend of individuals making and preferring online payments over more conventional payment methods like cash and checks. It's become more accessible and easier to fall victim to identity theft, phishing, and database breaches. Businesses spend much money on payment-security software to protect themselves from these kinds of threats and to boost security.
Security Concerns
Online payment methods are dangerous, as we saw in the last section. Inadequate security measures make it easy for criminals to access sensitive financial data and information. With no biometric or other identification verification mechanism in place, criminals can go free.
Technological Illiteracy
One major drawback of online payment systems is that many people, especially the older generation, need more technological literacy to use them effectively. They feel they need to be more confident making purchases online due to a need to understand using technology or devices. Many people use electronic payment systems sparingly because they find them too complicated. This is particularly problematic in economies in transition, such as India's.
Limitations on Amount and Time
To prevent abuse, several financial institutions cap the daily volume of transactions or the daily value of funds that can be transferred. Most financial dealings conducted online also have a deadline by which they must be completed (like receiving and accepting OTPs). All these restrictions may make the product less valuable to some users than they would like.
Service Fees and Other Additional Costs
Some services may charge users additional fees, such as for gateway installation or transaction processing if they choose to integrate online payment processing. Establishing online payment choices necessitates accessing the internet and the associated services. Sellers and buyers may find this an unnecessary source of stress and expense.
Disputed Transactions
You can report suspicious activity involving your electronic funds to your financial institution or the company that processed your online payment. It is only possible to make a complaint or get a refund if you can find the person's contact information or any other information on them. The scenario becomes complex.
Loss of Cards
Credit/debit cards, ATM cards, and national identification cards are used for most Internet transactions. Your associated online payment accounts will be immediately compromised if you lose any of these. Sure, you can call the bank and get your cards frozen if you lose them, but in the meantime, fraudsters could use your card to make purchases.
Identity Fraud
Online payments are more vulnerable to fraud because there is no method to verify the purchaser’s identity. Most online payments are made anonymously due to the need for more verification techniques, such as pictures or signatures. A great deal of forgeries and identity theft can result from this.
Market Analysis
Top 10 companies holding digital payments-related patents (From Orbit)
The Crucial Role of Patents in Digital Payments
Patents have become a crucial tool in protecting innovation in the world of digital payments. The first patent exclusively defining "Mobile Payment System" was filed in 2000 by Advance Tech International Ltd. Since then, patents have played an essential role in encouraging innovation and protecting inventors, which is vital for the growth and development of the digital payments industry. FinTech companies must focus on patent protection, as they invest significant time, energy, and money in developing new solutions. Please properly file or defend patents to avoid losing a competitive edge to second movers, which is why the fintech sector is currently experiencing a patent filing boom.
Conclusion
Every day, innovations are introduced into the payments market to make online purchases more convenient and quicker for consumers. Businesses may increase customer loyalty and satisfaction by providing many payment methods and completing the transaction process simply and safely. The global digital payment industry is forecast to reach $374.9 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 17.25% between n 2022 and 2030.
Author
Nishant Chopada
Associate Consultant at Lumenci
Nishant Chopada is an associate consultant at Lumenci with experience in mobile applications, medical devices, and wireless communication. His work at Lumenci focuses on Claim charting and product testing. He holds a Bachelor of Technology in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from the SRM Institute of Science and Technology.




