OpenRAN
Introduction
Currently, cell phone carriers must use proprietary equipment in building their networks. The radios and supporting equipment they use must be from the same vendor. With OpenRAN, these components no longer need to be from the same vendor, as OpenRAN will standardize the hardware and software connections between components to ensure interoperability. Standards-based equipment will allow carriers greater flexibility with their deployments and allow vendors to specialize in the equipment they provide. OpenRAN will also allow for the virtualization of network functions, separating hardware and software.
Radio Area Network
RAN stands for Radio Area Network, the portion of a carrier’s network beginning at the base station radio and transferring data to the core network. This network consists of the radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), and central unit (CU). The DU and CU combine traffic from their upstream connections and enable seamless cell phone roaming. OpenRAN standardizes the connections between these units allowing for cross-supplier interoperability.
Radio Area Network (Source: Lumenci)
Alliances and Standards Bodies
The standards body which creates standards for cell networks, 3GPP, also has relevant standards for RAN. However, these standards alone are not sufficient to ensure cross-compatibility, and other organizations exist to fill in this gap.
The two main alliances for OpenRAN are the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) and the O-RAN Alliance. The O-RAN Alliance focuses on making standards that permit cross-compatibility and improve the virtualization and automation of the RAN. TIP was founded before the O-RAN Alliance, and kickstarted the industry towards making an open RAN standard in the first place. TIP follows the standards created by the O-RAN Alliance. TIP now focuses on the deployment of OpenRAN compatible networks and conducts trials of the equipment to ensure compatibility. They also run an exchange, where OpenRAN compatible products are listed, and information provided for contacting their supplier. As well, they facilitate RFI submissions, by maintaining a RFI template and system for submission.
OpenRAN Reference Architecture
O-RAN Logical Architecture (Source: Lumenci)
The O-RAN alliance is working to define enough standards, to enable fully compliant RANs by the end of this year. Currently, they have published the “Open” Package, which consists of many of the core specifications needed to build a RAN. This includes many core networking specifications (Open fronthaul and network), and hardware specifications for equipment. As well, they published the Open stack, detailing a software reference design for the central and distributed units (O-CU/O-DU). This also provides the basis for future software design within the OpenRAN ecosystem.
The Open package also includes specifications for cloud applications and handling the complexities that come with the needed tight timing requirements, along with other details. The “Intelligent Package” will incorporate use cases that build upon the Open cloud, enabling dynamic optimizations that can deploy extra resources to where they are needed in a transparent and automatic manner. These optimizations will be powered by machine learning algorithms, and thanks to the interoperability that O-RAN enables, organizations will benefit from the ability to use the best-of-breed products for their application.
OpenRAN Compliant Product Suppliers
TIP maintains a robust list of hardware and software suppliers on their website. Some of the key players are Parallel Wireless, NOKIA, Mavenir, Ericsson, Cisco, and Huawei among other suppliers. Following the OpenRAN standard allows for all the equipment to be compatible, but there are often complex edge cases for RAN compatibility. When searching for a supplier, a key differentiating factor is their testing program. A robust testing program allows carriers to trust that the products they buy will work in their intended role. Regardless, the openness of OpenRAN allows for third parties to also participate in testing and determine the extent of any given products’ compatibility with O-RAN standards.
Benefits of OpenRAN
Benefits to Carriers
The carriers’ ability to optimize the construction of their RAN will be significantly enhanced by their ability to mix and match products from different suppliers. This flexibility will reduce the carriers’ reliance on any one supplier and improve the RAN quality by enabling carriers to choose the best equipment. There is also a potential for carriers to share RAN resources where it makes business sense or perhaps for a separate network operator to operate on behalf of multiple carriers.
Benefits to Consumers
The process of moving to an OpenRAN-compatible network should be transparent to the end users. OpenRAN will not change the characteristics of the radio communication between the phone and the network, but the advanced automation and optimization allowed by OpenRAN-compatible technologies will greatly improve the network experience. As well, the cost savings of OpenRAN will eventually help to reduce the expense of our cellular plans.
Use Cases
Automated Optimization
OpenRAN virtual appliances can take advantage of the benefits of software defined networking. The O-RAN specifications contain interfaces for automated optimization, allowing for the automated analysis of operational data to optimize the network operation. One of the RAN’s functions is to assign radio resources to clients connected to the network. Since the state of the art 5G implementations involve varying types of radios (eg. MIMO, Massive MIMO, Beam Forming) and spectrum (eg. Low, Mid, High band spectrum), creating static traffic policies is not an optimal solution. The solution that OpenRAN promises is to utilize AI/ML enhanced algorithms to continuously optimize the network.
Cloudification
Cloudification refers to the moving of RAN applications to the cloud. In this case, the “cloud” would likely not be a public cloud and would probably be a private infrastructure owned by the carrier. So really, cloudification refers to the ability to treat hardware and software independently, disaggregation as called by the industry. Developing cloud native RAN applications allows network operators to replace proprietary appliances with commodity hardware.
OpenRAN could also allow for new and/or enhanced services via the rapid deployment of edge cloud infrastructure. Edge cloud refers to cloud services being brought to smaller deployments closer to the end user. In the case of OpenRAN, the flexibility of the standard allows for some equipment to be virtualized as software appliances, specifically the DU and CU can be combined into a virtualized base-band unit (vBBU). The vBBU can then be run on commodity server hardware, with the only limitation being that it should be near to the radio to minimize latency. This development will encourage carriers to over-build the server capacity to allow for future expansion, and dynamic network optimization, and potentially lease the extra server capacity to cloud service providers. The cloud service providers could host content close to the consumers and provide a platform to deploy simple compute services to make apps and games quicker overall.
Open Interfaces
The flexibility permitted by OpenRAN allows for more innovation by suppliers focused on narrower fields. One of the major potentials this provides, is when it comes to the virtualization of the carrier’s network, as hinted at earlier. For example, carriers will be able to determine what type of network controller unit will work best for their network. For this unit specifically, there are many different approaches to take about optimizing the network. These units can do incredibly fast automatic optimizations via artificial intelligence technologies. Each supplier will have their own methods for attaining this, and this will provide for carriers to be able to determine what is best for their network. As carriers build out their 5G networks, this capability for automatic optimization will become increasingly important for providing an excellent customer experience.
Patent Activity
OpenRAN, while it is an open standard, does not prevent companies from protecting their intellectual property. OpenRAN sets standards for the interoperability for components, but not for their internal operation.
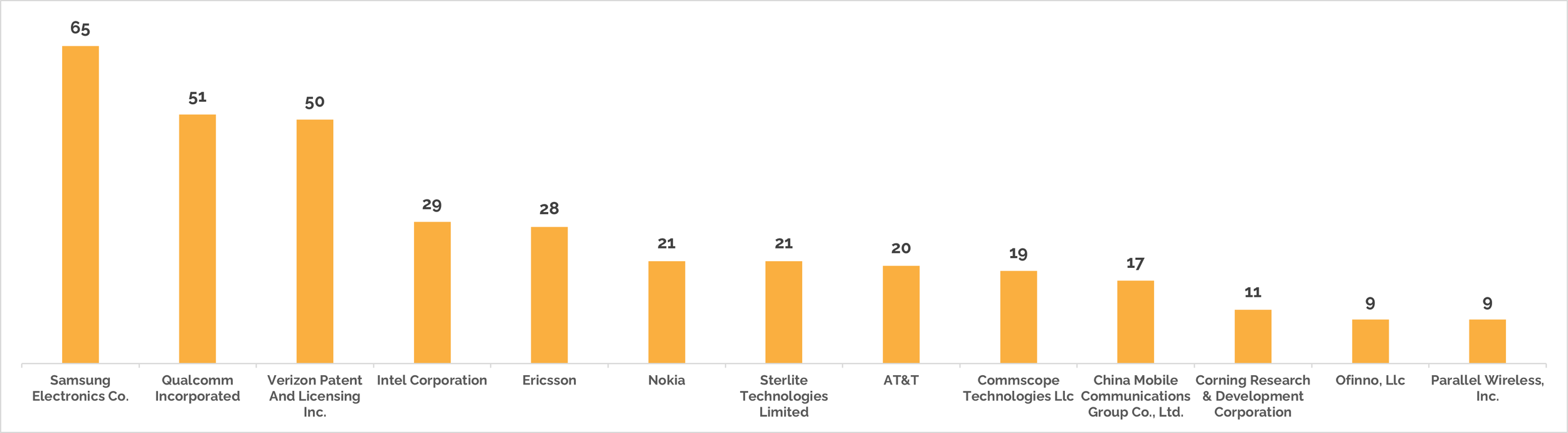
The chart below shows the top players in this field when looking at patent applications and grants:
Top Assignees for Patent Applications related to OpenRAN (Source: Lumenci)
*Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and is considered to be reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
*Disclaimer: This report is based on information that is publicly available and is considered to be reliable. However, Lumenci cannot be held responsible for the accuracy or reliability of this data.
Editorial Team at Lumenci
Through Lumenci blogs and reports, we share important highlights from the latest technological advancements and provide an in-depth understanding of their Intellectual Property (IP). Our goal is to showcase the significance of IP in the ever-evolving world of technology.