Storage Devices - Hardware Storage Solutions Popular Nowadays
Hardware storage solutions refer to the physical devices used to store and access data in a computer system. They use NAND flash memory technology for storage and operation. They can be divided into two categories, as given below.
Primary Storage Device
It is also known as internal and main memory. It holds program instructions, input data, and intermediate results. It is generally smaller in size. RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) are examples of primary storage.
Secondary Storage Device
It is a memory stored externally on the computer. It is mainly used for the permanent and long-term storage of programs and data. E.g., Hard Disk, SSD, optical storage devices, USB drives, and external hard drives. Various types of Secondary Storage Devices are explained briefly as follows-:
Hard Disk Drives (HDD): These are traditional storage devices that use spinning disks to store and access data. They are widely known and used for their large storage capacity, low cost, and easy compatibility with most PCs.
Solid State Drives (SSD): SSDs are a new trending storage device that uses flash memory to store data. It offers faster access times, lower power consumption, and better durability than HDDs. However, they are generally more expensive than HDDs.
USB drives: USB drives are small, portable storage devices that can be easily connected to a computer via a USB port. It is often used for transferring data from one computer to another or backing up important files.
Optical storage devices: These devices use lasers to read and write data to CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. These devices are commonly used for storing large amounts of multimedia content.
External hard drives: External hard drives are similar to internal hard drives but can be easily connected to a computer via a USB cable. They are commonly used for backup purposes or expanding a computer’s storage capacity. (Source 1)
HDD and SDD (Ref 2)
Advantages Of SSD
Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, which results in longer battery life and reduced energy consumption for laptops, PC’s and other electronic devices.
Reliability and Durability: SSDs have no moving parts and are less prone to failure due to mechanical problems. It is less affected by physical shocks and other harsh environmental conditions, thus making it more durable, i.e., having a long operation life.
Quiet Operation: SSDs make no noise due to the absence of moving parts, thus making them ideal for use in various quiet environments.
Speed: SSDs have faster read and write speeds than HDDs, which results in faster boot times, faster application launches, and improved overall system performance.
Types Of SSD
SATA SSDs: SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) SSDs are the most common and widely used SSDs in various electronic devices. They connect to the motherboard using the SATA interface and offer faster read and write speeds than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
PCIe SSDs: PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) SSDs are designed for high-performance applications such as gaming, video editing, and server use. These SSDs offer faster speeds, lower latency, and greater throughput than SAT SSDs.
NVMe SSDs: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs are the fastest SSDs available on the market. They use the PCIe interface and the NVMe protocol to deliver high speeds and low latency. They are preferred to be used in compute-intensive, high-end applications and enterprise servers.
SAS SSDs: SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) SSDs are designed for enterprise use and offer high performance, reliability, and data protection features. They connect to the server using the SAS interface and are available in various form factors, including 2.5-inch and U.2
Rugged SSDs: Rugged SSDs are designed for harsh environments, such as military, aerospace, and industrial applications. They offer shock and vibration resistance, extreme temperature tolerance, and high durability. Rugged SSDs are available in various form factors, including 2.5-inch, mSATA, and M.2.
Standards Of Storage Device
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a command and transport protocol that defines how the data is transferred between a PC motherboard and storage devices such as HDD and SSD. It is based on serial signaling technology. There are various revisions made in the SATA Standards by the SATA-IO (International Organization), a non-profit organization having various revisions such as SATA revisions 1,2,3.0-3.5 having variable data rates and applications.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a common motherboard interface used in computers' graphics cards, sound cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet hardware connections. It includes revisions from version 1.0-7.0.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface) is the specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media devices. It includes specifications of various versions, such as 1.0-2.0.
SAS(Serial-Attached SCSI) is a point-to-point serial protocol that moves data to and from computer-storage devices such as hard disk drives. It also offers optional compatibility with Serial ATA (SATA), versions 2 and later. It includes specifications of various versions, such as 1.0-5.0.
The SSD is classified based on form factors (i.e., size and configuration) as follows:
Types of SSD based on Form Factors (Ref 3)
2.5-Inch SSD:
2.5” is the most common type of SSD used in various desktop PCs etc. It has easy connectivity with the SATA interface and is easily adjusted and fitted into electronic devices.
M.2:
It is available in various lengths to enable different SSD drive capacities. It can have variable capacity drives depending on the requirements and NAND flash chips that can be mounted on it, thus, making it feasible for use in compact and slim devices.
mSATA SSD
mSATA, or mini-SATA, is a smaller version of the full-size SATA SSD. It uses a compact form factor like M.2 but doesn’t support interchangeable facilities. It supports both SATA and PCIe interface options. Its form factor is designed for smaller form factor systems where space is limited.U.2
It looks like a 2.5” drive but with more thickness. It is mainly used and reserved for high-end storage devices like workstations, servers, etc., requiring greater storage capacity.
Industry Outlook
The SSD plays a main role as a PC storage device. Some common companies that manufacture SSD are Samsung, Kingston, Crucial, Intel, and Seagate. These SSD are mainly used in various types of PCs, such as for gaming. One might have seen these companies using SSD nowadays. Other manufacturers are Adata, Corsair, Sabnet, and Plextor. (Source 3)
IP-Moats - Patent Trends for SSD
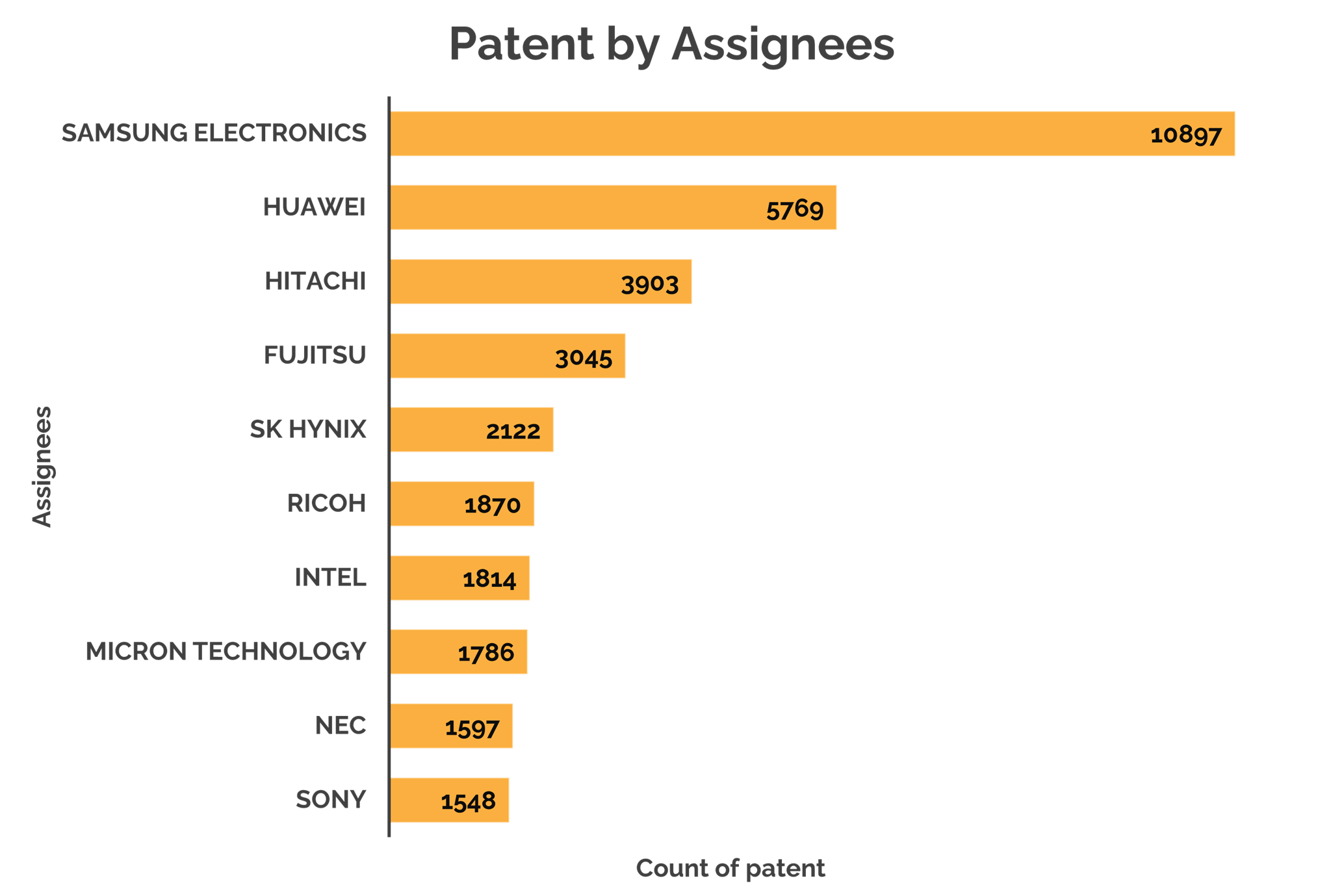
After doing the patent valuation, it can be observed from the figure that the top five assignees which have the largest patent portfolio related to SSD or Solid-State Drive are Samsung, followed by Huawei, Hitachi, Fujitsu, and SK Hynix. Samsung is also the main key player in the manufacturing or production of SSD.
While looking at the Yearly trends of Patent Filing related to the SSD or Solid-State Drives patented technology, it is observed that the maximum patent filing is done in the year 2018, followed by the year 2017.
*Data for the last two years might not be accurate due to unpublished applications.
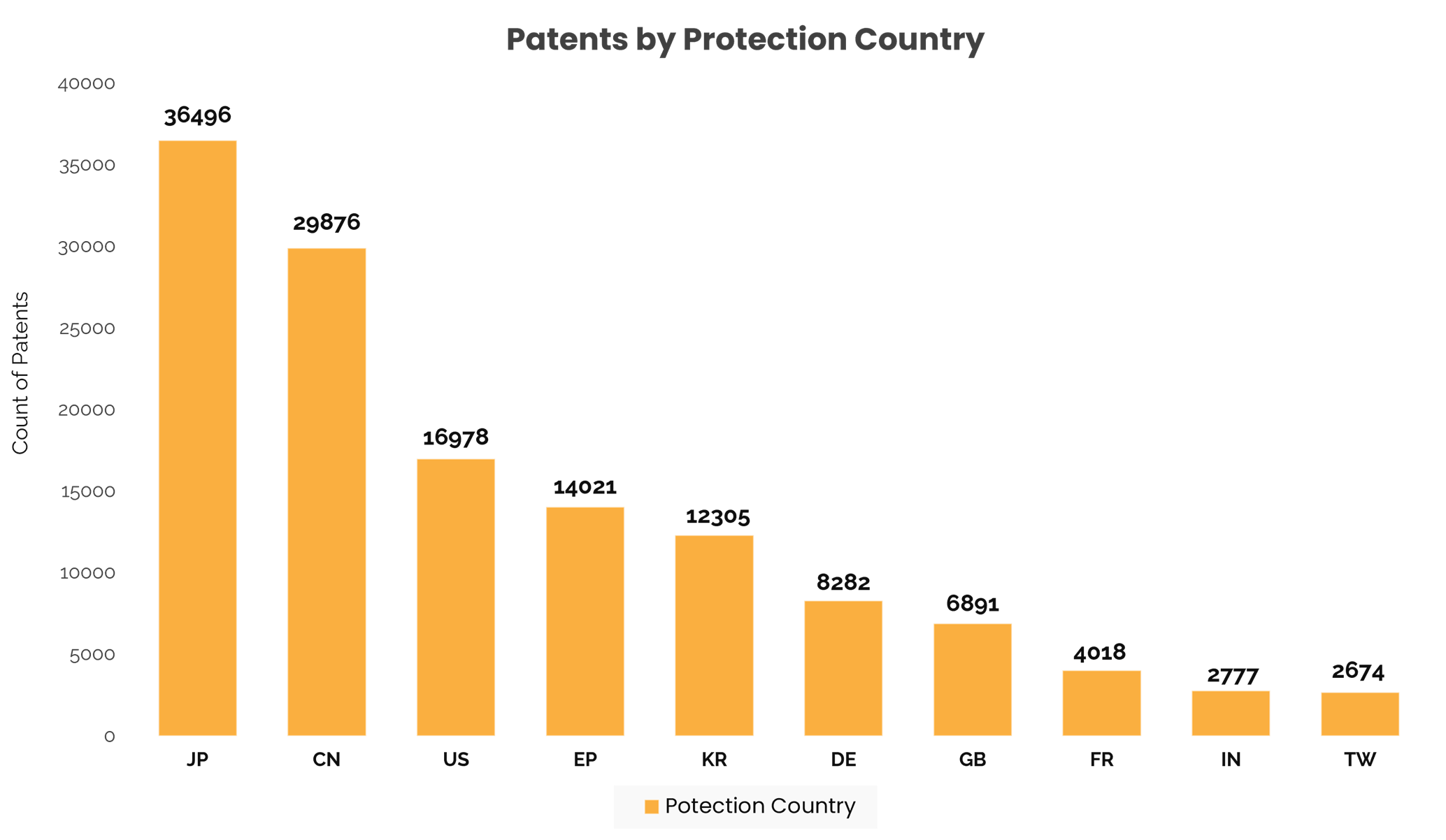
While looking at the patent protection or acquisition statistics by various countries, it is observed that Japan has the maximum number of patents filed under its jurisdiction, followed by China, the USA, and Europe, as shown in the adjacent figure.
*EP filings represent filings directly in the EPO office, and DE & GB represent filing in their respective offices.
In doing technology patent valuations, it is observed from the figure above that the major technological areas are computer technology, digital communication, and telecommunication, in which the top patent assignees fill patents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is observed that SSDs have several benefits over traditional HDDs, including faster performance, improved reliability, and long battery life, thus making them more preferably used in electronic devices. SSDs come in different types to meet the specific needs of users- SATA being the most common, while NVM etc., are used for applications requiring high performance. Thus, with different type of SSDs available, users can choose the right type that fits their requirements based on factors such as capacity, performance, cost, durability, and applications.
References:
Editorial Team at Lumenci
Through Lumenci blogs and reports, we share important highlights from the latest technological advancements and provide an in-depth understanding of their Intellectual Property (IP). Our goal is to showcase the significance of IP in the ever-evolving world of technology.